I found a nice visualisation of the most common 4-digit PIN numbers, based on 3.4 million PIN numbers from several data breaches: The 20 most common numbers make up 27% of the commonly used PIN numbers, i.e. from those 3.4 million PIN numbers used by people, more than a quarter were from this set of 20 PINs.
PIN Freq
#1 1234 10.713%
#2 1111 6.016%
#3 0000 1.881%
#4 1212 1.197%
#5 7777 0.745%
#6 1004 0.616%
#7 2000 0.613%
#8 4444 0.526%
#9 2222 0.516%
#10 6969 0.512%
#11 9999 0.451%
#12 3333 0.419%
#13 5555 0.395%
#14 6666 0.391%
#15 1122 0.366%
#16 1313 0.304%
#17 8888 0.303%
#18 4321 0.293%
#19 2001 0.290%
#20 1010 0.285%
A more detailed analysis is also provided, e.g. dates are also likely, either years or MMDD / DDMM (Month, Day / Day, Month).
Rule of thumb: what comes into your mind as easy to remember (e.g. birth dates) is what also comes into the mind of others -- and might therefore be tried by someone guessing your PIN code. So: do not use these!
I just stumbled over the 2024 Icelandic Developer Survey: Compensation, Technologies, and more that was based asking members of an Icelandic SW developer Facebook group to fill out a survey.
Having been involved in other IT-related survey's in Iceland (e.g.: The state of cybersecurity vulnerability reporting in Iceland), this is interesting work.
If page limit is an issue for you as an author of a scientific paper, then shortening references may be a way to squeeze out a few lines, e.g. using in the references section IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng. instead of IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering.
This is based on the ISO 4 standard: Words such as articles (the), conjunctions (and), and prepositions (for/of/in) are generally removed and a List of Title Word Abbreviations (LTWA) is used to abbreviate common title words.
You can look up the words in the LTWA at https://www.issn.org/services/online-services/access-to-the-ltwa/.
However, that list seems not be exhaustive: I have seen journals themselves using abbreviations not contained in the LTWA.
It therefore helps to search also for the full name and add as search term iso 4 or to check whether there is a Wikipedia article that contains the ISO 4 abbreviation or to look up the journal at https://www.resurchify.com/impact/details/ or at https://paperpile.com/guides/resources/abbreviations/
After successful two rounds of Cybersecurity grants for Icelandic SME companies, Icelandic Smaller and Middle-size Enterprises (SMEs) can now for a third time apply for cybersecurity-related funding. The call topics are the same as last time:
- strengthening cybersecurity culture and awareness,
- efficient education, research and development,
- secure digital services and innovation,
- stronger law enforcement, defense and national security,
- effective response to incidents, and
- strong infrastructure, technology and legal framework.
This funding is in the context of the ECCC/EU co-funded project Eyvör – the National Cybersecurity Coordination Centre of Iceland (NCC-IS). See also the official web page of Eyvör NCC-IS.


For teaching (and for my eyes on a 4K screen), I need sometimes the Eclipse IDE with larger icons and UI fonts (while the editor fonts can be easily adjusted within the Eclipse preferences, namely by adjusting Text Font, the icons cannot and while the UI fonts should be adjustable via Gnome settings, this did not work on my KDE/Plasma system).
What works for me (with X11 -- Wayland is a different thing) is described in https://linux-blog.anracom.com/2024/08/28/eclipse-too-small-icons-on-high-dpi-screens-workaround-for-kde-plasma-by-scaling-on-x11-and-wayland/
I also have in my home directory a .gtkrc-2.0 file and need to find out whether deleting it would change anything (i.e. global KDE/Plasma font size setting might then be used, but as long as .gtkrc-2.0 exists, this might override the KDE/Plasma font size setting) -- same applies for the gnome-tweaks command.
On Saturday, 27. September 2024, 12:00-17:00, there was Vísindavaka 2025, the Icelandic family-friendly-during-daytime edition of European Researchers' Night 2026 at Laugardalshöll in Reykjavik.

The Computer Science department of University of Iceland had a couple of booths there, showcasing our activities in a way accessible for the general public.

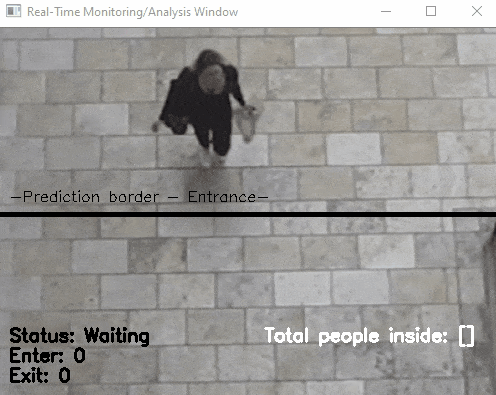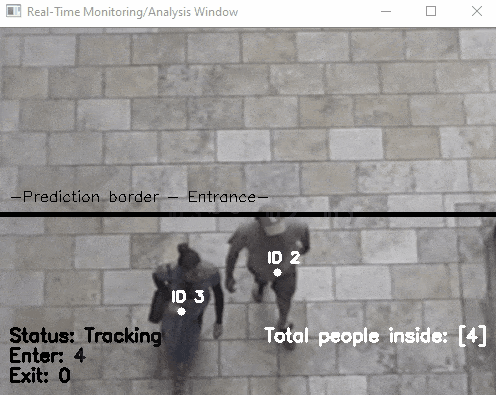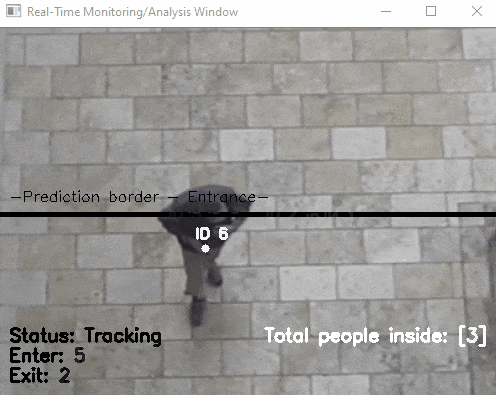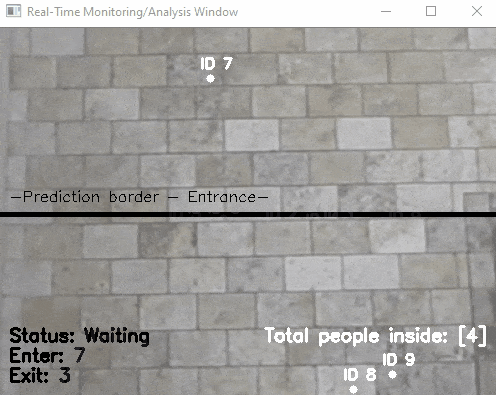 Another application of object detection (combined with object tracking): the organisers of the European Researcher's Night asked me to count the number of visitors by having a camera at the entrance that counts people entering and exiting. This was not showcased at a booth, but ran GDPR compliant (counting was done in real time and no video was recorded) in the background. As the camera was low resolution, the software had however some issues and was more reliable in counting people exiting than entering. Anecdotal evidence suggest, that children were not counted as these were simply too few pixels to be detected. It remains to be found out whether a higher resolution camera would improve the situation.
Another application of object detection (combined with object tracking): the organisers of the European Researcher's Night asked me to count the number of visitors by having a camera at the entrance that counts people entering and exiting. This was not showcased at a booth, but ran GDPR compliant (counting was done in real time and no video was recorded) in the background. As the camera was low resolution, the software had however some issues and was more reliable in counting people exiting than entering. Anecdotal evidence suggest, that children were not counted as these were simply too few pixels to be detected. It remains to be found out whether a higher resolution camera would improve the situation.

Beat the AI! A remote sensing demonstration that relates also to work done in EDIH-IS and IHPC where neural networks are used to classify land cover from satellite images, (Photo from Vísindavaka 2022)
Our booths at the previous European Researchers' Nights:
Parts of this event are in the context of our cybersecurity activities and the ECCC/EU co-funded projects ICEDEF – Defend Iceland and Eyvör – the National Cybersecurity Coordination Centre of Iceland (NCC-IS).


Eyvör NCC-IS, the National Coordination Centre for Cybersecurity in Iceland, where University of Iceland is a member, is holding on 11 September 2025, 08:30-12:30, an event on Cybersecurity: From Grants to Impact (registration needed). Those who got grants from Eyvör NCC-IS for increasing cybersecurity will present their results.
The Icelandic minister for infrastructure and the director of the European Cybersecurity Competence Centre and Network (ECCC) will attend and the agenda is:
08:30 Coffee & Registration
09:00 Opening – Mr. Hrafnkell Gíslason, Managing Director of ECOI
09:10 Eyjólfur Ármannsson, Minister of Infrastructure
09:20 Luca Tagliaretti, Executive Director at ECCC
09:50 Hörn Valdimarsdóttir covers the Defend Iceland success story
10:00 Break
10:10 Grant Projects: Brief Presentations, first part
11:00 Break – Coffee and refreshments
11:20 Grant Projects: Brief Presentations, second part
12:05 Eyjólfur Eyfells at Rannís covers the Application Process and Eligibility
12:30 Closing
The next call for grants will be open 1. October to 1. December 2025: check out at Rannís.

Photo from after the event: Eyvör NCC-IS members (and Fulbright Visiting Scholar) together with ECCC executive director Luca Tagliaretti
This event is in the context of our cybersecurity activities and the ECCC/EU co-funded projects ICEDEF – Defend Iceland and Eyvör – the National Cybersecurity Coordination Centre of Iceland (NCC-IS).


While I am teaching to use AI coding assistants (and emphasize the pros and cons, in particular that it helps only if you have enough knowledge to judge whether the output is correct or pure hallucination), there have been recently two studies published that give an indication that AI coding assistants do actually decrease productivity:
One aspect is that developers learn over time about the project that they are working on whereas LLMs have been trained once and will always start from scratch in a project where they are used as coding assistants.
A personal idea for future research: as there have been reports about AI slob (e.g. AI generates low-quality documents that get distributed and then take time to read and therefore, this reduces in the end productivity), it might be worthwhile to measure the impact of AI coding assistants on maintainability: if AI coding assistance would produce code that is hard to maintain, then any gains by AI coding assistants might get eaten up in future when it comes to maintenance.
We presented an update on our cybersecurity activities to industry and students at the 21st Icelandic HPC Community Workshop August 28, 2025.
We covered there the joint MSc. programme in cybersecurity, our research, and the Digital Europe Programme projects Eyvör NCC-IS, the National Coordination Centre for Cybersecurity in Iceland and Defend Iceland, including the European network of NCCs and the European Cybersecurity Competence Centre (ECCC).



This event is in the context of our cybersecurity activities and the ECCC/EU co-funded projects ICEDEF – Defend Iceland and Eyvör – the National Cybersecurity Coordination Centre of Iceland (NCC-IS).


On 11th of July 2025, participants of the Children's university (Háskóli unga fólksins) visited the Computer Science department. We did there a mini tabletop exercise on critical infrastructure in Iceland and after that authentication was discussed, e.g.:
- use different passwords for different services -- do not use the same password everywhere (if your password got stolen, it will by tried at all kinds of other web pages, so if you use the same password everywhere, all other services can be accessed using your identity,
- use two factor authentication: even if your password got stolen, an attacker would still need the second authentication factor, e.g., would need to steal your phone that contains some authentication app as second factor in addition to your password.

This event is in the context of our cybersecurity activities and the ECCC/EU co-funded projects ICEDEF – Defend Iceland and Eyvör – the National Cybersecurity Coordination Centre of Iceland (NCC-IS).
















